
What is LNG, and how can is support our energy needs?
You might’ve seen LNG mentioned in the news recently, especially when it comes to energy supply and electricity pricing. But what is it, and how does it fit into the energy story for Aotearoa?
What is LNG?
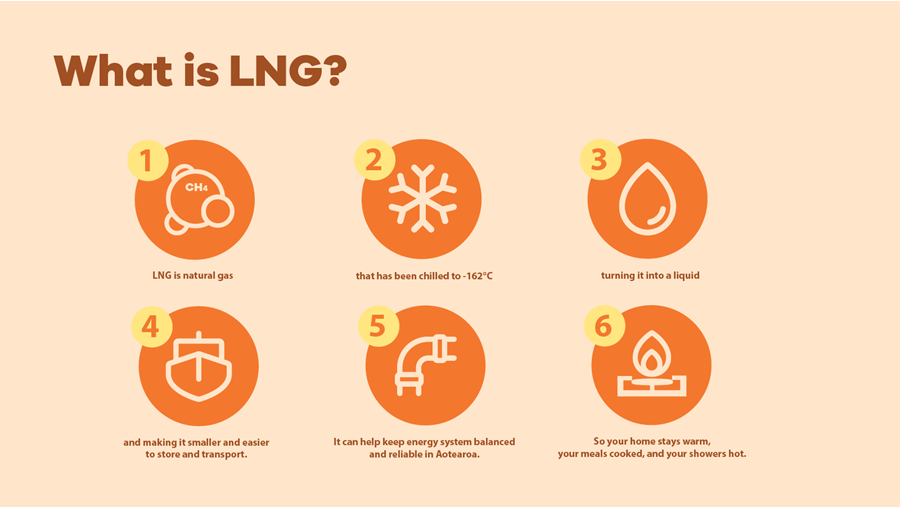
LNG stands for Liquefied Natural Gas. It’s the same natural gas many of us already use for cooking, heating and hot water, but cooled to around –162°C, almost three times colder than Antarctica, until it becomes a liquid.
At that temperature, gas takes up about 600 times less space. Think of it like fitting everything in your garage into a single suitcase. That compact size makes LNG much easier to transport and store, helping to keep supply steady when demand is high.
So basically, it’s cold and compact!
Why does it matter?
Aotearoa is still producing its own natural gas, most of which is used to energise industries, and at times generate electricity, while households use only a small share each year. Bringing in LNG to New Zealand when needed can help keep supply balanced across the whole network, making sure there’s plenty of energy to keep homes warm, meals cooked and showers hot.
LNG can also be used as a backup energy source to create electricity when renewables like hydro and wind are running low. Topping up the supply helps keep our energy system balanced and reliable, especially during times of high electricity demand.
What’s the difference between natural gas and LNG?
Not much, really. Natural gas flows through your pipes at home, heating your water, cooking your meals and keeping you warm. LNG is that same gas, just in liquid form for easier transport. Once it’s warmed back up, it turns back into the same natural gas we use every day.
Where does it come from?
Natural gas has been an important part of New Zealand’s energy story for decades, and it still has a role to play as we transition towards renewable options such as biomethane.
Natural gas - Most of New Zealand’s natural gas comes from the Taranaki region, where it’s piped across the North Island to energise homes, businesses and industries.
LNG - In times when renewable energy is lower, imported LNG can help balance supply. It supports everything from electricity generation and large energy users like hospitals and factories, right through to everyday households.
How it helps keep Aotearoa energised
Whether it’s domestic natural gas, or imported LNG, both can play an important role in keeping Aotearoa energised. Natural Gas plays a big role in filling the gaps when renewable energy can’t keep up, like when the wind doesn’t blow, the sun isn’t shining or lake levels are low.
For Kiwi households, natural gas brings instant hot water, controllable heat for cooking and cosy warm homes. For businesses, gas energises everything from restaurants and manufacturing plants to pottery kilns and the bakery ovens that bring us our iconic mince and cheese pies.
Looking ahead
As Aotearoa transitions toward renewable energy, natural gas continues to provide a reliable, flexible energy source. In the future, it could sit alongside renewable gases like biomethane, with LNG playing a supporting role to keep supply steady and our energy system running smoothly.
Natural gas is already a big part of the energy story of Aotearoa, and as we move toward a lower-emissions future, LNG could help keep that story balanced.
Ready to connect?
Check out the connection process, to know what choices you'll need to make as part of getting connected to natural gas.
Submit your natural gas connection application today. Our customer team will then ring you to confirm a few more details and progress your application.
Want to know more?
If you've had a good look around our website and still have questions let us know what you'd like more information about.
